With the latest release, ProtectUSB got an image mode in addition to its existing folder/file based production flow. Using the image mode is preferable to the file mode in case of USB sticks with a large number of files, because in that case it significantly speeds up the process.
Important: Using the image mode with regular packaged content without additional files does not make sense and is significantly slower than the folder/file based production.
When you are reading this, chances are, that you are already using ProtectUSB for copy protection or that you are at least interested in doing so. But did you know that you can also do regular USB stick duplication? With regular (unprotected) content and without any cost. This blog post is about how this works.
In this blog post I’ll try to give you some advice about how to select the right file system for your USB stick content/duplication.
Most of you will be aware of FAT32, exFAT and NTFS but what the advantages and disadvantages of each file system are, is not so clear. I’ll try to shed some light on this, so you can make the best choice.
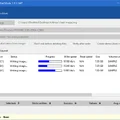
The current file system of each connected USB stick is always displayed in the list view.
Our ProtectUSB solutions for content and software are used by the top USB duplication services around the globe. For these services, the solution of choice must come at a reasonable cost, be reliable, fast and must keep manual work at lowest levels.
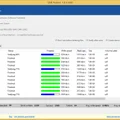
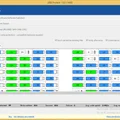
To achieve this, ProtectUSB is capable of handling large amounts of USB sticks in parallel. For example, the picture you see below shows one of our tests boards, which features 8 USB hubs with 13 ports each (incl. power supplies). After cascading, one of these boards result in 99 sticks being written in parallel (in this case connected …